Tilaiya Dam


Tilaiya Dam was the first of the four multi-purpose dams included in the first phase of the Damodar Valley Corporation. It was constructed across the Barakar River, at Tilaiya in Koderma district in the Indian state of Jharkhand and opened in 1953.
DVC overview




5miles
Wildlife
Sanctuary


Dam














M: municipality, CT: census town, R: rural/ urban centre, D: dam, P: power plant, T: tourist centre
Owing to space constraints in the small map, the actual locations in a larger map may vary slightly
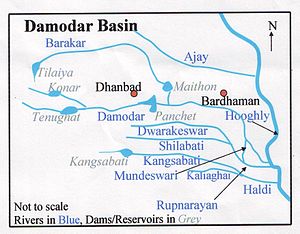
The valley of the Damodar River was flood prone and the devastating flood of 1943, lead to the formation of the high-powered ”Damodar Flood Enquiry Committee” by the government of Bengal. The committee recommended the formation of a body similar to the Tennessee Valley Authority of the United States. Subsequently, W.L. Voorduin, a senior engineer of TVA, was appointed to study the problem. He suggested the multi-purpose development of the valley as a whole in 1944. Damodar Valley Corporation was set up in 1948 as “the first multipurpose river valley project of independent India.”[1]
The first dam was built across the Barakar River at Tilaiya and inaugurated in 1953. The second dam, Konar Dam, across the Konar River was inaugurated in 1955. The third dam across the Barakar River at Maithon was inaugurated in 1957. The fourth dam across the Damodar at Panchet was inaugurated in 1959.[2]
DVC was formed with the central government and the governments of Bihar (later Jharkhand) and West Bengal participating in it. The main aims of the corporation were flood control, irrigation, generation and transmission of electricity, and year-round navigation. The corporation was also expected to provide indirect support for the over-all development of the region. However, while Voorduin had proposed the construction of eight dams, DVC built only four.[3]
The dam
Tilaiya Dam was built across the Barakar River, a tributary of the Damodar River, about 130 miles (210 km) above the point of confluence.[3] It is only 64.4 kilometres (40.0 mi) from its source. At the point where the dam has been built, the river passes through a narrow gorge, with hills rising steeply on both the sides. It is a concrete gravity dam with a maximum height of 30.2 metres (99 ft), while the hills on both the sides rise to a height of about 45.7 metres (150 ft). The spillway has 14 crest gates. There are 2 modified sluice gates at a lower level for release of water during the dry season. The reservoir is spread over an area of 5,921 hectares (14,630 acres).[4]

Tilaiya Dam was inaugurated on 21 February 1953. It has a power generation capacity of 2 x 2 MW.[2]
The main (Patna-Ranchi) road from Barhi on Grand Trunk Road passing through hills overlooking the reservoir is picturesque.[5]
Postal stamp
The Indian Postal Service issued a set of four stamps for the Five-Year Plan series on 26 January 1955, that included one stamp of one anna value depicting Tilaiya Dam. Shortly after opening the Tilaiya dam, pictured on the one-anna stamp, Nehru commented in a letter to the chief ministers that "the sight of those works filled me, as it did others who were present, with a sense of great achievement."[6]
References
- ^ "Overview". DVC. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ^ a b "Damodar Valley Corporation". Dams and Barrages. DVC. Archived from the original on 29 April 2010. Retrieved 6 June 2010.
- ^ a b Planning in India by Mahesh Chand, Vinay Kumar Puri, pages 422-423, Allied Publishers Private Ltd. ISBN 81-7023-058-6
- ^ Hydrology and Water Resources of India by Sharad K. Jain, Pushpendra K. Agarwal and Vijay P.Singh, page 394: Tilaiya Reservoir , Springer
- ^ "Tilaiya Dam". Koderma district administration. Retrieved 2010-06-10.
- ^ Wyatt, Andrew (2005-10-30). "Do our stamps evoke nationalism?". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Archived from the original on 2 November 2005. Retrieved 10 June 2010.
- v
- t
- e
| Damodar basin | |
|---|---|
| Subarnarekha basin | |
| Brahmani basin | |
| Son basin |
|
| Others: north flowing | |
| Others: east flowing |
|
| Others: south-east flowing |












