| IGF2 |
|---|
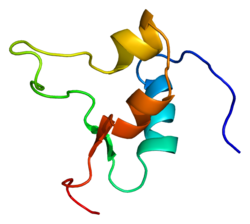 |
| Structure de la protéine IGF2. Basé sur l'identifiant PDB 1igl. |
| Structures disponibles |
|---|
| PDB | Recherche d'orthologue: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| Identifiants PDB |
|---|
3KR3, 1IGL, 2L29, 2V5P, 3E4Z |
|
|
| Identifiants |
|---|
| Aliases | IGF2 |
|---|
| IDs externes | OMIM: 147470 MGI: 96434 HomoloGene: 510 GeneCards: IGF2 |
|---|
| Position du gène (Homme) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 11 humain[1] |
|---|
| | Locus | 11p15.5 | Début | 2,129,112 bp[1] |
|---|
| Fin | 2,158,391 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Position du gène (Souris) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 7 (souris)[2] |
|---|
| | Locus | 7 F5|7 87.99 cM | Début | 142,204,503 bp[2] |
|---|
| Fin | 142,220,553 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| Expression génétique |
|---|
| Bgee | | Humain | Souris (orthologue) |
|---|
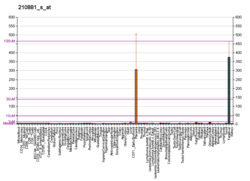
| Fortement exprimé dans | - placenta
- nerf sural
- stromal cell of endometrium
- right lobe of liver
- apex of heart
- left uterine tube
- muscle de la cuisse
- right uterine tube
- endocol
- ventricule gauche
|
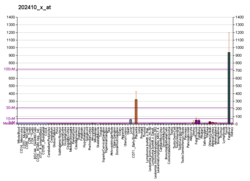
| | Fortement exprimé dans | - extraembryonic membrane
- Vésicule vitelline
- tubercule génital
- placenta
- tail of embryo
- tube neural
- dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation granule cell
- intra-embryonic coelom
- rhombencéphale
- mésencéphale
|
| | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | Plus de données d'expression de référence |
|
|---|
|
| Gene Ontology |
|---|
| Fonction moléculaire | - insulin receptor binding
- hormone activity
- liaison protéique
- growth factor activity
- insulin-like growth factor receptor binding
- integrin binding
- protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity
- receptor ligand activity
| | Composant cellulaire | - région extracellulaire
- platelet alpha granule lumen
- milieu extracellulaire
| | Processus biologique | - regulation of gene expression by genetic imprinting
- skeletal system development
- insulin receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- ostéogenèse
- platelet degranulation
- développent d'un organisme multicellulaire
- glucose metabolic process
- positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division
- positive regulation of cell division
- positive regulation of MAPK cascade
- positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation
- positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- métabolisme des glucides
- regulation of signaling receptor activity
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- osteoblast differentiation
- in utero embryonic development
- embryonic placenta development
- positive regulation of protein phosphorylation
- positive regulation of cell population proliferation
- morphogenèse d'un organe animal
- exocrine pancreas development
- regulation of histone modification
- insulin receptor signaling pathway via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- positive regulation of multicellular organism growth
- positive regulation of catalytic activity
- positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway
- positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
- striated muscle cell differentiation
- regulation of muscle cell differentiation
- embryonic placenta morphogenesis
- positive regulation of glycogen (starch) synthase activity
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologues |
|---|
| Espèces | Homme | Souris |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001291862
NM_000612
NM_001007139
NM_001127598
NM_001291861 |
| |
|---|
NM_001122736
NM_001122737
NM_010514
NM_001315488
NM_001315489 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protéine) | |
|---|
NP_000603
NP_001007140
NP_001121070
NP_001278790
NP_001278791 |
| |
|---|
NP_001116208
NP_001116209
NP_001302417
NP_001302418
NP_034644 |
|
|---|
| Localisation (UCSC) | Chr 11: 2.13 – 2.16 Mb | Chr 7: 142.2 – 142.22 Mb |
|---|
| Publication PubMed | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| Voir/Editer Humain | Voir/Editer Souris |
|

 Portail de la biochimie
Portail de la biochimie