Sino-Austronesian languages
| Sino-Austronesian | |
|---|---|
| (hypothetical) | |
| Geographic distribution | East, South and Southeast Asia |
| Linguistic classification | proposed language family |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | None |
Sino-Austronesian or Sino-Tibetan-Austronesian is a proposed language family suggested by Laurent Sagart in 1990.[1] Using reconstructions of Old Chinese, Sagart argued that the Austronesian languages are related to the Sinitic languages phonologically, lexically and morphologically. Sagart later accepted the Sino-Tibetan languages as a valid group and extended his proposal to include the rest of Sino-Tibetan.[2] He also placed the Tai–Kadai languages within the Austronesian family as a sister branch of Malayo-Polynesian.[3] The proposal has been largely rejected by other linguists who argue that the similarities between Austronesian and Sino-Tibetan more likely arose from contact rather than being genetic.[4][5][6]
Classification
Sagart (2004)
The classification below follows Sagart (2004).
- Sino-Austronesian (Sino-Tibetan–Austronesian)
Sagart suggests that monosyllabic Old Chinese words correspond to the second syllables of disyllabic Proto-Austronesian roots. However, the type A/B distinction in OC, corresponding to non-palatalized or palatalized syllables in Middle Chinese, is considered to correspond to a voiceless/voiced initial in PAN.
| Gloss | Proto-Austronesian | Chinese |
|---|---|---|
| brain | *punuq | 腦 *anuʔ > nǎo |
| salt | *siRaH1 | 鹵 *araʔ > lǔ |
| foxtail millet | *beCeng | 稷 *btsək > jì |
Starosta (2005)
Stanley Starosta (2005) expands Sagart's Sino-Austronesian tree with a "Yangzian" branch, consisting of Austroasiatic and Hmong–Mien, to form an East Asian superphylum.[7]
Criticism
Weera Ostapirat (2005) supports the link between Austronesian and Kra–Dai (Sagart built upon Ostapirat's findings), though as sister groups. However, he rejects a link to Sino-Tibetan, noting that the apparent cognates are rarely found in all branches of Kra–Dai, and almost none are in core vocabulary.[8]
Austronesian linguists Paul Jen-kuei Li and Robert Blust have criticized Sagart's comparisons, on the grounds of loose semantic matches, inconsistent correspondences, and that basic vocabulary is hardly represented. They also note that comparing with the second syllable of disyllabic Austronesian roots vastly increases the odds of chance resemblance.[4][5] Blust has been particularly critical of Sagart's use of the comparative method.[9] Laurent Sagart (2016) responds to some of the criticisms by Blust (2009).[10]
Alexander Vovin (1997) does not accept Sino-Austronesian as a valid grouping, but instead suggests that some of the Sino-Austronesian parallels proposed by Sagart may in fact be due to an Austronesian substratum in Old Chinese.[6] This view is also espoused by George van Driem, who suggests that Austronesian and Sinitic had come into contact with each other during the fourth and third millennia BC in the Longshan interaction sphere.[11][12][13]
Distributions
-
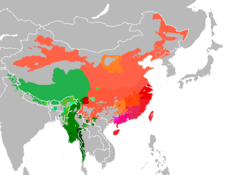 Distribution of Sino-Tibetan languages
Distribution of Sino-Tibetan languages -
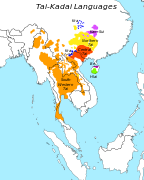 Distribution of Tai–Kadai languages
Distribution of Tai–Kadai languages -
 Dispersal of Austronesian languages
Dispersal of Austronesian languages
See also
- Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages
- Dené–Caucasian languages (Sino-Caucasian)
- Mainland Southeast Asia linguistic area
- Haplogroup O (Y-DNA)
- Languages of China
References
- ^ Sagart, L. (1990) "Chinese and Austronesian are genetically related". Paper presented at the 23rd International Conference on Sino-Tibetan Languages and Linguistics, October 1990, Arlington, Texas.
- ^ Sagart, Laurent (2005). "Sino-Tibetan–Austronesian: an updated and improved argument". In Sagart, Laurent; Blench, Roger; Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia (eds.). The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London: Routledge Curzon. pp. 161–176. ISBN 978-0-415-32242-3.
- ^ Sagart, Laurent (2004). "The higher phylogeny of Austronesian and the position of Tai-Kadai". Oceanic Linguistics. 43 (2): 411–444. doi:10.1353/ol.2005.0012. JSTOR 3623364. S2CID 49547647.
- ^ a b Li, Paul Jenkuei (1995). "Is Chinese genetically related to Austronesian?". In Wang, William S-Y. (ed.). The Ancestry of the Chinese Language. Journal of Chinese Linguistics Monograph Series. Vol. 8. Chinese University Press. pp. 92–112. JSTOR 23826144.
- ^ a b Blust, Robert (1995). "An Austronesianist looks at Sino-Austronesian". In Wang, William S-Y. (ed.). The Ancestry of the Chinese Language. Journal of Chinese Linguistics Monograph Series. Vol. 8. Chinese University Press. pp. 283–298. JSTOR 23826144.
- ^ a b Vovin, Alexander (1997). "The comparative method and ventures beyond Sino-Tibetan". Journal of Chinese Linguistics. 25 (2): 308–336. JSTOR 23756693.
- ^ Starosta, Stanley (2005). "Proto-East Asian and the origin and dispersal of languages of east and southeast Asia and the Pacific". In Sagart, Laurent; Blench, Roger; Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia (eds.). The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London: Routledge Curzon. pp. 182–197. ISBN 978-0-415-32242-3.
- ^ Ostapirat, Weera (2005). "Kra–Dai and Austronesian: Notes on phonological correspondences and vocabulary distribution". In Sagart, Laurent; Blench, Roger; Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia (eds.). The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. London: Routledge Curzon. pp. 107–131. ISBN 978-0-415-32242-3.
- ^ Blust, Robert (2014). "Some Recent Proposals Concerning the Classification of the Austronesian Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 53 (2): 300–391. doi:10.1353/ol.2014.0025. JSTOR 43286532. S2CID 144931249.
- ^ Sagart, Laurent (2016). "The wider connections of Austronesian: A response to Blust (2009)". Diachronica. 33 (2): 255–281. doi:10.1075/dia.33.2.04sag.
- ^ van Driem, G. 1998. ‘Neolithic correlates of ancient Tibeto-Burman migrations’, pp. 67–102 in Roger Blench and Matthew Spriggs, eds., Archaeology and Language II. London: Routledge.
- ^ van Driem, G. 2005. ‘Sino-Austronesian vs. Sino-Caucasian, Sino-Bodic vs. Sino-Tibetan, and Tibeto-Burman as default theory’, pp. 285–338 in Yogendra Prasada Yadava, Govinda Bhattarai, Ram Raj Lohani, Balaram Prasain and Krishna Parajuli, eds., Contemporary Issues in Nepalese Linguistics. Kathmandu: Linguistic Society of Nepal.
- ^ van Driem, George. 2016. ‘The Eastern Himalayan corridor in prehistory’, pp. 467-524, Vol. II in Elena Nikolaevna Kolpačkova, ed., Проблемы китайского и общего языкознания — Problems in Chinese and General Linguistics. St. Petersburg: Izdatel’stvo Studija « NP-Print ».
Further reading
- Blust, Robert (2013). The Austronesian languages (revised ed.). Canberra: Australian National University. hdl:1885/10191. ISBN 978-1-922185-07-5.
- Miyake, Marc. 2015. Proto-Sino-Tibetan-Austronesian *ponuq 'brain'?
- Miyake, Marc. 2015. Do Austronesian and Sino-Tibetan share a word for Setaria italica?
- Sagart, Laurent (1994). "Proto-Austronesian and the Old Chinese evidence for Sino-Austronesian". Oceanic Linguistics. 33 (2): 271–308. doi:10.2307/3623130. JSTOR 3623130.
- Sagart, Laurent (2016). "The wider connections of Austronesian: a response to Blust". Diachronica. 33 (2): 255–281. doi:10.1075/dia.33.2.04sag.
External links
 Media related to Sino-Austronesian languages at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Sino-Austronesian languages at Wikimedia Commons- Laurent Sagart's list of Old Chinese words at the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database
- v
- t
- e
(Himachal, Uttarakhand, Nepal, Sikkim)
| Greater Magaric |
|---|

(Tibet, Bhutan, Arunachal)
| "Naga" | |
|---|---|
| Sal |
| Burmo-Qiangic |
|---|
(Arunachal)
| Greater Siangic |
|
|---|














