Plane (Unicode)
In the Unicode standard, a plane is a contiguous group of 65,536 (216) code points. There are 17 planes, identified by the numbers 0 to 16, which corresponds with the possible values 00–1016 of the first two positions in six position hexadecimal format (U+hhhhhh). Plane 0 is the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP), which contains most commonly used characters. The higher planes 1 through 16 are called "supplementary planes".[1] The last code point in Unicode is the last code point in plane 16, U+10FFFF. As of Unicode version 15.1, five of the planes have assigned code points (characters), and seven are named.
The limit of 17 planes is due to UTF-16, which can encode 220 code points (16 planes) as pairs of words, plus the BMP as a single word.[2] UTF-8 was designed with a much larger limit of 231 (2,147,483,648) code points (32,768 planes), and would still be able to encode 221 (2,097,152) code points (32 planes) even under the current limit of 4 bytes.[3]
The 17 planes can accommodate 1,114,112 code points. Of these, 2,048 are surrogates (used to make the pairs in UTF-16), 66 are non-characters, and 137,468 are reserved for private use, leaving 974,530 for public assignment.
Planes are further subdivided into Unicode blocks, which, unlike planes, do not have a fixed size. The 328 blocks defined in Unicode 15.1 cover 26% of the possible code point space, and range in size from a minimum of 16 code points (sixteen blocks) to a maximum of 65,536 code points (Supplementary Private Use Area-A and -B, which constitute the entirety of planes 15 and 16). For future usage, ranges of characters have been tentatively mapped out for most known current and ancient writing systems.[4]
Overview
- v
- t
- e
| Basic | Supplementary | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plane 0 | Plane 1 | Plane 2 | Plane 3 | Planes 4–13 | Plane 14 | Planes 15–16 | |||
| 0000–FFFF | 10000–1FFFF | 20000–2FFFF | 30000–3FFFF | 40000–DFFFF | E0000–EFFFF | F0000–10FFFF | |||
| Basic Multilingual Plane | Supplementary Multilingual Plane | Supplementary Ideographic Plane | Tertiary Ideographic Plane | unassigned | Supplementary Special-purpose Plane | Supplementary Private Use Area planes | |||
| BMP | SMP | SIP | TIP | — | SSP | SPUA-A/B | |||
| 0000–0FFF | 8000–8FFF | 10000–10FFF | 18000–18FFF | 20000–20FFF | 28000–28FFF | 30000–30FFF | E0000–E0FFF | 15: SPUA-A | |
Assigned characters
| Plane | Allocated code points[note 1] version 15.0 | Assigned characters |
|---|---|---|
| 0 BMP | 65,520 | 55,639 |
| 1 SMP | 26,160 | 23,276 |
| 2 SIP | 61,536 | 61,495 |
| 3 TIP | 9,136 | 9,131 |
| 14 SSP | 368 | 337 |
| 15 SPUA-A | 65,536 | 0 (by definition) |
| 16 SPUA-B | 65,536 | 0 (by definition) |
| Totals | 293,792 | 149,878 |
- ^ Code points which have been allocated to a Unicode block.
Basic Multilingual Plane

The first plane, plane 0, the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP), contains characters for almost all modern languages, and a large number of symbols. A primary objective for the BMP is to support the unification of prior character sets as well as characters for writing. Most of the assigned code points in the BMP are used to encode Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) characters.
The High Surrogate (U+D800–U+DBFF) and Low Surrogate (U+DC00–U+DFFF) codes are reserved for encoding non-BMP characters in UTF-16 by using a pair of 16-bit codes: one High Surrogate and one Low Surrogate. A single surrogate code point will never be assigned a character.
65,520 of the 65,536 code points in this plane have been allocated to a Unicode block, leaving just 16 code points in a single unallocated range (2FE0..2FEF).
As of Unicode 15.1[update], the BMP comprises the following 164 blocks:
- Alphabetic left-to-right scripts:
- Basic Latin (Lower half of ISO/IEC 8859-1: ISO/IEC 646:1991-IRV aka ASCII) (0000–007F)
- Latin-1 Supplement (Upper half of ISO/IEC 8859-1) (0080–00FF)
- Latin Extended-A (0100–017F)
- Latin Extended-B (0180–024F)
- IPA Extensions (0250–02AF)
- Spacing Modifier Letters (02B0–02FF)
- Combining Diacritical Marks (0300–036F)
- Greek and Coptic (0370–03FF)
- Cyrillic (0400–04FF)
- Cyrillic Supplement (0500–052F)
- Armenian (0530–058F)
- Semitic abjads and other right-to-left scripts:
- Hebrew (0590–05FF)
- Arabic (0600–06FF)
- Syriac (0700–074F)
- Arabic Supplement (0750–077F)
- Thaana (0780–07BF)
- N'Ko (07C0–07FF)
- Samaritan (0800–083F)
- Mandaic (0840–085F)
- Syriac Supplement (0860–086F)
- Arabic Extended-B (0870–089F)
- Arabic Extended-A (08A0–08FF)
- Brahmic scripts:
- Devanagari (0900–097F)
- Bengali (0980–09FF)
- Gurmukhi (0A00–0A7F)
- Gujarati (0A80–0AFF)
- Oriya (0B00–0B7F)
- Tamil (0B80–0BFF)
- Telugu (0C00–0C7F)
- Kannada (0C80–0CFF)
- Malayalam (0D00–0D7F)
- Sinhala (0D80–0DFF)
- Thai (0E00–0E7F)
- Lao (0E80–0EFF)
- Tibetan (0F00–0FFF)
- Myanmar (1000–109F)
- Other alphabetic or syllabic left-to-right scripts:
- Georgian (10A0–10FF)
- Hangul Jamo (1100–11FF)
- Ethiopic (1200–137F)
- Ethiopic Supplement (1380–139F)
- Cherokee (13A0–13FF)
- Unified Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics (1400–167F)
- Ogham (1680–169F)
- Runic (16A0–16FF)
- Philippine scripts:
- Tagalog (1700–171F)
- Hanunoo (1720–173F)
- Buhid (1740–175F)
- Tagbanwa (1760–177F)
- Khmer (1780–17FF)
- Mongolian (1800–18AF)
- Unified Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics Extended (18B0–18FF)
- Brahmic scripts:
- Limbu (1900–194F)
- Tai scripts:
- Tai Le (1950–197F)
- New Tai Lue (1980–19DF)
- Khmer Symbols (19E0–19FF)
- Buginese (1A00–1A1F)
- Tai Tham (1A20–1AAF)
- Combining Diacritical Marks Extended (1AB0–1AFF)
- Indonesian scripts:
- Balinese (1B00–1B7F)
- Sundanese (1B80–1BBF)
- Batak (1BC0–1BFF)
- Lepcha (1C00–1C4F)
- Ol Chiki (1C50–1C7F)
- Other left-to-right alphabetic or syllabic supplements:
- Cyrillic Extended-C (1C80–1C8F)
- Georgian Extended (1C90–1CBF)
- Sundanese Supplement (1CC0–1CCF)
- Vedic Extensions (1CD0–1CFF)
- Other left-to-right alphabetic supplements:
- Phonetic Extensions (1D00–1D7F)
- Phonetic Extensions Supplement (1D80–1DBF)
- Combining Diacritical Marks Supplement (1DC0–1DFF)
- Latin Extended Additional (1E00–1EFF)
- Greek Extended (1F00–1FFF)
- Symbols:
- General Punctuation (2000–206F)
- Superscripts and Subscripts (2070–209F)
- Currency Symbols (20A0–20CF)
- Combining Diacritical Marks for Symbols (20D0–20FF)
- Letterlike Symbols (2100–214F)
- Number Forms (2150–218F)
- Arrows (2190–21FF)
- Mathematical Operators (2200–22FF)
- Miscellaneous Technical (2300–23FF)
- Control Pictures (2400–243F)
- Optical Character Recognition (2440–245F)
- Enclosed Alphanumerics (2460–24FF)
- Box Drawing (2500–257F)
- Block Elements (2580–259F)
- Geometric Shapes (25A0–25FF)
- Miscellaneous Symbols (2600–26FF)
- Dingbats (2700–27BF)
- Miscellaneous Mathematical Symbols-A (27C0–27EF)
- Supplemental Arrows-A (27F0–27FF)
- Braille Patterns (2800–28FF)
- Supplemental Arrows-B (2900–297F)
- Miscellaneous Mathematical Symbols-B (2980–29FF)
- Supplemental Mathematical Operators (2A00–2AFF)
- Miscellaneous Symbols and Arrows (2B00–2BFF)
- Other left-to-right alphabetic scripts or supplements:
- Glagolitic (2C00–2C5F)
- Latin Extended-C (2C60–2C7F)
- Coptic (2C80–2CFF)
- Georgian Supplement (2D00–2D2F)
- African scripts:
- Tifinagh (2D30–2D7F)
- Ethiopic Extended (2D80–2DDF)
- Other left-to-right alphabetic supplements:
- Cyrillic Extended-A (2DE0–2DFF)
- Supplemental Punctuation (2E00–2E7F)
- CJK scripts and symbols:
- CJK Radicals Supplement (2E80–2EFF)
- Kangxi Radicals (2F00–2FDF)
- Ideographic Description Characters (2FF0–2FFF)
- CJK Symbols and Punctuation (3000–303F)
- Hiragana (3040–309F)
- Katakana (30A0–30FF)
- Bopomofo (3100–312F)
- Hangul Compatibility Jamo (3130–318F)
- Kanbun (3190–319F)
- Bopomofo Extended (31A0–31BF)
- CJK Strokes (31C0–31EF)
- Katakana Phonetic Extensions (31F0–31FF)
- Enclosed CJK Letters and Months (3200–32FF)
- CJK Compatibility (3300–33FF)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension A (3400–4DBF)
- Yijing Hexagram Symbols (4DC0–4DFF)
- CJK Unified Ideographs (4E00–9FFF)
- Yi Syllables (A000–A48F)
- Yi Radicals (A490–A4CF)
- Lisu (A4D0–A4FF)
- African scripts:
- Vai (A500–A63F)
- Other left-to-right alphabetic supplements:
- Cyrillic Extended-B (A640–A69F)
- African scripts:
- Bamum (A6A0–A6FF)
- Other left-to-right alphabetic supplements:
- Modifier Tone Letters (A700–A71F)
- Latin Extended-D (A720–A7FF)
- Brahmic scripts:
- Syloti Nagri (A800–A82F)
- Common Indic Number Forms (A830–A83F)
- Phags-pa (A840–A87F)
- Saurashtra (A880–A8DF)
- Devanagari Extended (A8E0–A8FF)
- Kayah Li (A900–A92F)
- Rejang (A930–A95F)
- Hangul Jamo Extended-A (A960–A97F)
- Brahmic scripts:
- Javanese (A980–A9DF)
- Myanmar Extended-B (A9E0–A9FF)
- Cham (AA00–AA5F)
- Myanmar Extended-A (AA60–AA7F)
- Tai Viet (AA80–AADF)
- Meetei Mayek Extensions (AAE0–AAFF)
- Ethiopic Extended-A (AB00–AB2F)
- Latin Extended-E (AB30–AB6F)
- Cherokee Supplement (AB70–ABBF)
- Meetei Mayek (ABC0–ABFF)
- Hangul Syllables (AC00–D7AF)
- Hangul Jamo Extended-B (D7B0–D7FF)
- Surrogates:
- High Surrogates (D800–DB7F)
- High Private Use Surrogates (DB80–DBFF)
- Low Surrogates (DC00–DFFF)
- Private Use Area (E000–F8FF)
- CJK Compatibility Ideographs (F900–FAFF)
- Alphabetic Presentation Forms (FB00–FB4F)
- Arabic Presentation Forms-A (FB50–FDFF)
- Variation Selectors (FE00–FE0F)
- Vertical Forms (FE10–FE1F)
- Combining Half Marks (FE20–FE2F)
- CJK Compatibility Forms (FE30–FE4F)
- Small Form Variants (FE50–FE6F)
- Arabic Presentation Forms-B (FE70–FEFF)
- Halfwidth and Fullwidth Forms (FF00–FFEF)
- Specials (FFF0–FFFF)
Supplementary Multilingual Plane

Plane 1, the Supplementary Multilingual Plane (SMP), contains historic scripts (except CJK ideographic), and symbols and notation used within certain fields. Scripts include Linear B, Egyptian hieroglyphs, and cuneiform scripts. It also includes English reform orthographies like Shavian and Deseret, and some modern scripts like Osage, Warang Citi, Adlam, Wancho and Toto. Symbols and notations include historic and modern musical notation; mathematical alphanumerics; shorthands; Emoji and other pictographic sets; and game symbols for playing cards, mahjong, and dominoes.
As of Unicode 15.1[update], the SMP comprises the following 151 blocks:
- Archaic Greek and other left-to-right scripts:
- Linear B Syllabary (10000–1007F)
- Linear B Ideograms (10080–100FF)
- Aegean Numbers (10100–1013F)
- Ancient Greek Numbers (10140–1018F)
- Ancient Symbols (10190–101CF)
- Phaistos Disc (101D0–101FF)
- Lycian (10280–1029F)
- Carian (102A0–102DF)
- Coptic Epact Numbers (102E0–102FF)
- Old Italic (10300–1032F)
- Gothic (10330–1034F)
- Old Permic (10350–1037F)
- Ugaritic (10380–1039F)
- Old Persian (103A0–103DF)
- Deseret (10400–1044F)
- Shavian (10450–1047F)
- Osmanya (10480–104AF)
- Osage (104B0–104FF)
- Elbasan (10500–1052F)
- Caucasian Albanian (10530–1056F)
- Vithkuqi (10570–105BF)
- Linear A (10600–1077F)
- Latin Extended-F (10780–107BF)
- Right-to-left scripts:
- Cypriot Syllabary (10800–1083F)
- Imperial Aramaic (10840–1085F)
- Palmyrene (10860–1087F)
- Nabataean (10880–108AF)
- Hatran (108E0–108FF)
- Phoenician (10900–1091F)
- Lydian (10920–1093F)
- Meroitic Hieroglyphs (10980–1099F)
- Meroitic Cursive (109A0–109FF)
- Kharoshthi (10A00–10A5F)
- Old South Arabian (10A60–10A7F)
- Old North Arabian (10A80–10A9F)
- Manichaean (10AC0–10AFF)
- Avestan (10B00–10B3F)
- Inscriptional Parthian (10B40–10B5F)
- Inscriptional Pahlavi (10B60–10B7F)
- Psalter Pahlavi (10B80–10BAF)
- Old Turkic (10C00–10C4F)
- Old Hungarian (10C80–10CFF)
- Hanifi Rohingya (10D00–10D3F)
- Rumi Numeral Symbols (10E60–10E7F)
- Yezidi (10E80–10EBF)
- Arabic Extended-C (10EC0–10EFF)
- Old Sogdian (10F00–10F2F)
- Sogdian (10F30–10F6F)
- Old Uyghur (10F70–10FAF)
- Chorasmian (10FB0–10FDF)
- Elymaic (10FE0–10FFF)
- Brahmic scripts:
- Brahmi (11000–1107F)
- Kaithi (11080–110CF)
- Sora Sompeng (110D0–110FF)
- Chakma (11100–1114F)
- Mahajani (11150–1117F)
- Sharada (11180–111DF)
- Sinhala Archaic Numbers (111E0–111FF)
- Khojki (11200–1124F)
- Multani (11280–112AF)
- Khudawadi (112B0–112FF)
- Grantha (11300–1137F)
- Newa (11400–1147F)
- Tirhuta (11480–114DF)
- Siddham (11580–115FF)
- Modi (11600–1165F)
- Mongolian Supplement (11660–1167F)
- Takri (11680–116CF)
- Ahom (11700–1174F)
- Dogra (11800–1184F)
- Warang Citi (118A0–118FF)
- Dives Akuru (11900–1195F)
- Nandinagari (119A0–119FF)
- Zanabazar Square (11A00–11A4F)
- Soyombo (11A50–11AAF)
- Unified Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics Extended-A (11AB0–11ABF)
- Brahmic scripts:
- Pau Cin Hau (11AC0–11AFF)
- Devanagari Extended-A (11B00–11B5F)
- Bhaiksuki (11C00–11C6F)
- Marchen (11C70–11CBF)
- Masaram Gondi (11D00–11D5F)
- Gunjala Gondi (11D60–11DAF)
- Makasar (11EE0–11EFF)
- Kawi (11F00–11F5F)
- Lisu Supplement (11FB0–11FBF)
- Tamil Supplement (11FC0–11FFF)
- Cuneiform scripts:
- Cuneiform (12000–123FF)
- Cuneiform Numbers and Punctuation (12400–1247F)
- Early Dynastic Cuneiform (12480–1254F)
- Cypro-Minoan (12F90–12FFF)
- Hieroglyphic scripts:
- Egyptian Hieroglyphs (13000–1342F)
- Egyptian Hieroglyph Format Controls (13430–1345F)
- Anatolian Hieroglyphs (14400–1467F)
- Bamum Supplement (16800–16A3F)
- Mro (16A40–16A6F)
- Tangsa (16A70–16ACF)
- Bassa Vah (16AD0–16AFF)
- Pahawh Hmong (16B00–16B8F)
- Medefaidrin (16E40–16E9F)
- Miao (16F00–16F9F)
- East Asian scripts:
- Ideographic Symbols and Punctuation (16FE0–16FFF)
- Tangut (17000–187FF)
- Tangut Components (18800–18AFF)
- Khitan Small Script (18B00–18CFF)
- Tangut Supplement (18D00–18D7F)
- Kana Extended-B (1AFF0–1AFFF)
- Kana Supplement (1B000–1B0FF)
- Kana Extended-A (1B100–1B12F)
- Small Kana Extension (1B130–1B16F)
- Nushu (1B170–1B2FF)
- Notational writing systems:
- Duployan (1BC00–1BC9F)
- Shorthand Format Controls (1BCA0–1BCAF)
- Symbols and numerals:
- Musical notation:
- Znamenny Musical Notation (1CF00–1CFCF)
- Byzantine Musical Symbols (1D000–1D0FF)
- Musical Symbols (1D100–1D1FF)
- Ancient Greek Musical Notation (1D200–1D24F)
- Kaktovik Numerals (1D2C0–1D2DF)
- Mayan Numerals (1D2E0–1D2FF)
- Mathematical symbols:
- Tai Xuan Jing Symbols (1D300–1D35F)
- Counting Rod Numerals (1D360–1D37F)
- Mathematical Alphanumeric Symbols (1D400–1D7FF)
- Musical notation:
- Notational writing systems:
- Sutton SignWriting (1D800–1DAAF)
- Other left-to-right scripts:
- Latin Extended-G (1DF00–1DFFF)
- Glagolitic Supplement (1E000–1E02F)
- Cyrillic Extended-D (1E030–1E08F)
- Nyiakeng Puachue Hmong (1E100–1E14F)
- Toto (1E290–1E2BF)
- Wancho (1E2C0–1E2FF)
- Nag Mundari (1E4D0–1E4FF)
- African scripts:
- Ethiopic Extended-B (1E7E0–1E7FF)
- Mende Kikakui (1E800–1E8DF)
- Adlam (1E900–1E95F)
- Symbols and numerals:
- Indic Siyaq Numbers (1EC70–1ECBF)
- Ottoman Siyaq Numbers (1ED00–1ED4F)
- Arabic Mathematical Alphabetic Symbols (1EE00–1EEFF)
- Game tiles and cards:
- Mahjong Tiles (1F000–1F02F)
- Domino Tiles (1F030–1F09F)
- Playing Cards (1F0A0–1F0FF)
- Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement (1F100–1F1FF)
- Enclosed Ideographic Supplement (1F200–1F2FF)
- Miscellaneous Symbols and Pictographs (1F300–1F5FF)
- Emoticons (1F600–1F64F)
- Ornamental Dingbats (1F650–1F67F)
- Transport and Map Symbols (1F680–1F6FF)
- Alchemical Symbols (1F700–1F77F)
- Geometric Shapes Extended (1F780–1F7FF)
- Supplemental Arrows-C (1F800–1F8FF)
- Supplemental Symbols and Pictographs (1F900–1F9FF)
- Chess Symbols (1FA00–1FA6F)
- Symbols and Pictographs Extended-A (1FA70–1FAFF)
- Symbols for Legacy Computing (1FB00–1FBFF)
Supplementary Ideographic Plane

Plane 2, the Supplementary Ideographic Plane (SIP), is used for CJK Ideographs, mostly CJK Unified Ideographs, that were not included in earlier character encoding standards.
As of Unicode 15.1[update], the SIP comprises the following seven blocks:
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension B (20000–2A6DF)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension C (2A700–2B73F)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension D (2B740–2B81F)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension E (2B820–2CEAF)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension F (2CEB0–2EBEF)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension I (2EBF0–2EE5F)
- CJK Compatibility Ideographs Supplement (2F800–2FA1F)
Tertiary Ideographic Plane
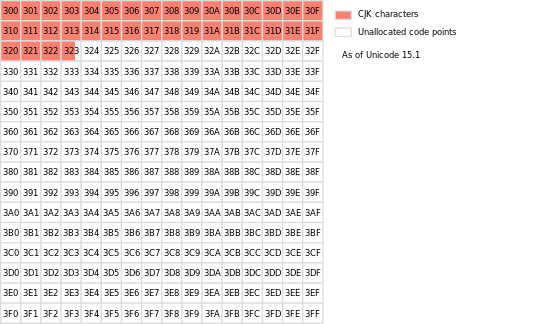
Plane 3 is the Tertiary Ideographic Plane (TIP). CJK Unified Ideographs Extension G was added to the TIP in Unicode 13.0, released in March 2020.[5] It also is tentatively allocated for Oracle Bone script and Small Seal Script.[6]
As of Unicode 15.1[update], the TIP comprises the following two blocks:
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension G (30000–3134F)
- CJK Unified Ideographs Extension H (31350–323AF)
Unassigned planes
Planes 4 to 13 (planes 4 to D in hexadecimal): No characters have yet been assigned, or proposed for assignment, to Planes 4 through 13.
Supplementary Special-purpose Plane

Plane 14 (E in hexadecimal) is designated as the Supplementary Special-purpose Plane (SSP). It comprises the following two blocks, as of Unicode 15.1[update]:
- Tags (E0000–E007F)
- Variation Selectors Supplement (E0100–E01EF) – used to indicate alternate glyphs for characters.
Private Use Area Planes
The two planes 15 and 16 (planes F and 10 in hexadecimal) each contain a "Private Use Area". They contain blocks named Supplementary Private Use Area-A (PUA-A) and -B (PUA-B). The Private Use Areas are available for use by parties outside ISO and Unicode (private character encoding).
References
- ^ "Glossary". www.unicode.org. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ^ See Table 3.5 "UTF-16 Bit Distribution" in the Unicode Standard https://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode6.0.0/UnicodeStandard-6.0.pdf
- ^ See Table 3.6 "UTF-8 Bit Distribution" in the Unicode Standard https://www.unicode.org/versions/Unicode6.0.0/UnicodeStandard-6.0.pdf
- ^ "Roadmaps to Unicode". www.unicode.org. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ^ "Announcing The Unicode Standard, Version 13.0".
- ^ "Proposed New Characters: The Pipeline". www.unicode.org.











